Titan – AN7: Implementing a Modbus TCP – Modbus RTU gateway
¿Buscas alguna otra cosa?
Table of Contents
Scenario Details
The Titan routers include all the typical features of a 2G/3G/4G router. However, they also include a series of additional features that help make it one of the leading market routers based on the number of features it includes.
One of these additional features is the ability to create up to five simultaneous IP-RS232/RS485/USB gateways. Examples include:
Ethernet <> RS232/RS485/USB
Wi-Fi <> RS232/RS485/USB
3G/4G <> RS232/RS485/USB
Using these gateways, we can specify that the Titan router uses Modbus RCP – Modbus RTU protocol. We will see a basic example of how to use the MTX-Router-Titan-3G-mini device (or any other Titan router models) to implement a Modbus TCP – Modbus RTU gateway.
Description of the Example
In this example we will configure the MTX-Router-Titan-3G-mini device to create a 3G-RS485 gateway (with Modbus TCP – Modbus RTU protocol) in order to gain access to a remote PLC with an RS485 port. To do this, we will use a COM1 port and the Modbus TCP 502 port will be awaiting responses.
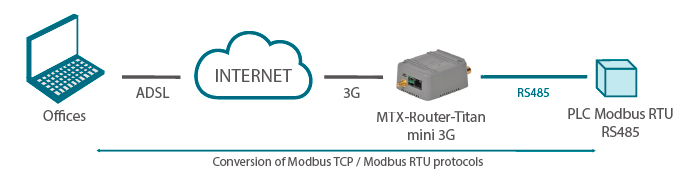
(Image: Modbus RTU PLC device with an RS485 port; Modbus TCP/Modbus RTU protocol conversion)
Configuring 3G Communications
Configuring 3G communications is simple. We simply must indicate the APN, login and password (and PIN if necessary) at the “Wan > Basic Settings” menu, as shown below:

Configuring the Associated RS232 Port
Since we will use the COM1 port to access the RS485 device, we will have to access the following configuration screen at: “Serial Settings > Serial Port1-232/485”, using the configuration shown in the screen below. It is supposed that the PLC has a configuration of 115200,8,n,1. We must select the “Serial IP – Gateway (Modbus TCP / Modbus RTU)” gateway, choosing the 502 port as the TCP port awaiting response.

Also, since we will use the COM1 port as an RS485, we must select the RS485 box, as shown in the previous screen. Additionally, we must configure the microswitches situated next to the SIM card holder on the MTX-Router-Titan-3G-mini device in order to adjust the hardware so that it works in RS485 mode. As the user manual shows, microswitches 3 and 4 must be switched to ON.

Pins 7 and 3 on the MTX-Router-Titan-3G-mini device’s DB15 connectors must have the RS485 port set to D+ and D- respectively.
| FDB15 CONNECTOR | FUNCTION |
| 1 | CANH |
| 2 | COM1__RX |
| >3 | COM1__TX / RS485_D- |
| 4 | COM3__TX |
| 5 | RELAY1__NC |
| 6 | CANL |
| >7 | COM1__RTS / RS485_D+ |
| 8 | COM1__CTS |
| 9 | COM3__RX |
| 10 | VCC_OUT (*2) |
| 11 | RELAY1_COM |
| 12 | COM2__TX |
| 13 | COM2__RX/DIGITAL__INPUT (*3) |
| 14 | GND |
| 15 | RELAY1__NA |
Points to Consider
- For such a scenario in which both gateways are used in server mode, a SIM card with a fixed IP address should be used. An alternative option is to use DynDNS. To configure DynDNS, use the menu: Other > DynDNS
- If you do not have a SIM with a fixed IP address, or if your network provider uses NAT (which uses private IP addresses such as 10.X.X.X), meaning you cannot use DynDNS, you can activate the OpenVPN option (menu “VPN > OpenVPN Client”). If you use OpenVPN, you will not need a fixed IP address nor DynDNS; however, you will have to configure OpenVPN on your company’s server. An Application Note detailing how to configure OpenVPN for Titan routers is available.
- If you require that only authorized IP addresses can access the serial gateways, configure the menu “Firewall > Authorized IPs”, specifying the authorized IP addresses, and selecting that this be applied for “Serial Gateways”.

- In this example, we have used a 3G communications interface; however, it is also possible to use a gateway with Ethernet or WiFi communications. If you do not wish to use 3G, you can also use the MTX-Router-Titan-mini (only Ethernet & WiFi) device, which is a more economic option given it does not contain the 3G module.
