The MTX-Router-Titan II, MTX-Router-Titan and MTX-Router-Titan mini devices are ready to read, store and send registers from Waveflow 868MHz pulse counters as well as WaveTherm 868MHz temperature sensors. An internal Wavecard 868MHz communication card can be included, allowing for communications with Wavenis devices up to 1km away (in direct vision), or up to 16km away using up to 3 boosters. When using the MTX-Router-Titan-mini model to read Waveflows, a Waveport (USB or RS232) device is required.
An Application Note is available for a greater understanding of its use, including examples (AN6-RouterTitan-Metering-Wavenis-Concentrator.pdf).
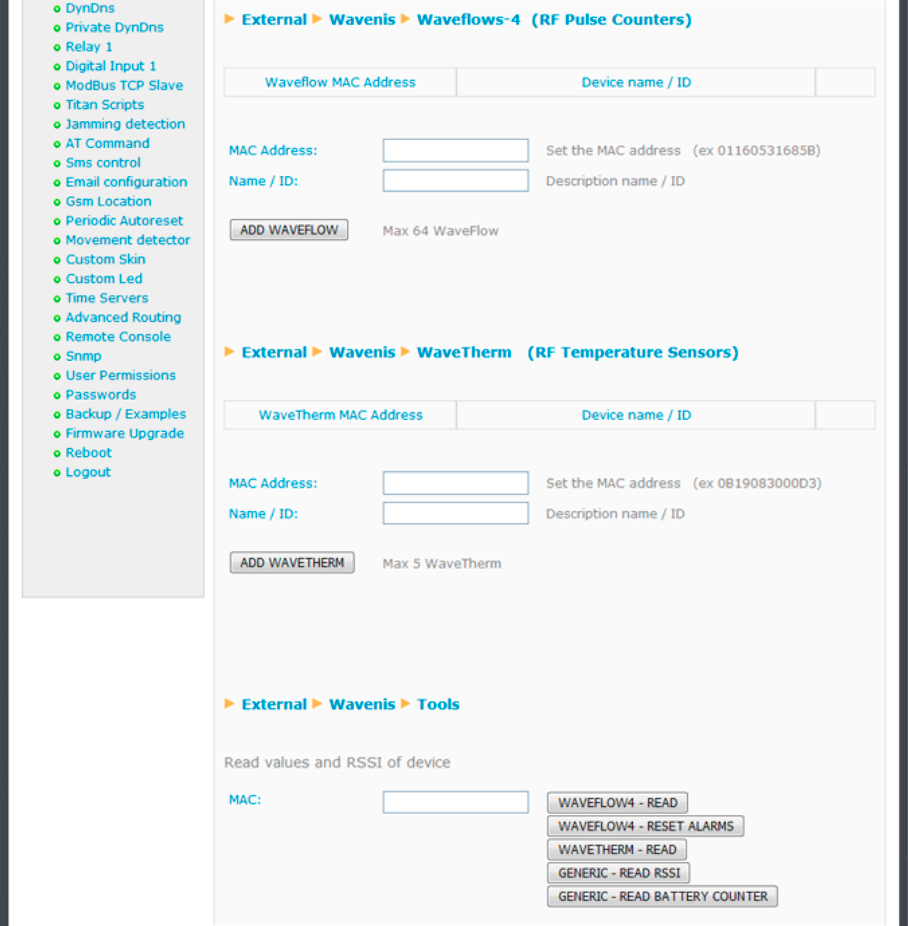
Periodic readings of up to 64 Waveflow devices and 5 Wavetherm devices can be programmed, sending at a later time the readings to a webserver via a JSON object or via the logger using FTP.
- Enabled: activate this option to enable Waveflow communications
- Serial Port: select the serial port “Serial Port 4 – TTL” for the Titan router and “Serial Port 5 – USB” when using the Titan-mini model
- Period: in this field, indicate how frequently (in minutes) we wish the data sensors to be read
- Number of attempts: in this field we can specify the number of attempts to take readings should an error occur
- Logger: select this option if we wish for the internal logger to be used to store the Modbus registers that are read (for later sending to the web platform)
External Devices: Wavenis, WaveTalk
This section allows we to configure up to 10 Wavetalk boosters. Remember that up to three boosters can be used between the Wavenis concentrator (the Titan router) and the sensors to be read. Here the MAC address of each WaveTalk booster should be specified.
External Devices: Wavenis, Waveflow-4
The following configuration parameters allow we to add Waveflow devices. Up to 64 can be added.
- Name/ID: name to identify a Waveflow device
- MAC address: Waveflow device’s MAC address (hexadecimal format)
If we wish to use boosters, this must be done by inputting the MAC address of the device to be used with boosters in the “MAC address” field. For example, if we wish to use boosters 2 and 5 for the Waveflow device with MAC address 010203040506, we would insert ‘010203040506;2;5’ (remember that semicolons are used for separation).
External Devices: Wavenis, Wavetherm
The following configuration parameters allow we to add Wavetherm devices. Up to 5 can be added.
- Name/ID: name to identify a Wavetherm device
- MAC Address: Wavetherm device’s MAC address (hexadecimal format)
If we wish to use boosters, this must be done by inputting the MAC address of the device to be used with boosters in the “MAC address” field. For example, if we wish to use boosters 2 and 5 for the Wavetherm device with MAC address 010203040506, we would insert ‘010203040506;2;5’ (remember that semicolons are used for separation)
External Devices: Wavenis, Tools
In this section we will find tools to remotely access Wavenis devices at any time. Simply input the device’s MAC address (with boosters if applicable), and press the corresponding button.
- Waveflow-4 read: reading of the count, alarms and battery status of a Waveflow device with 4 entries
- Waveflow-4 reset Alarms: if alarms are used (battery, circuit shortage, etc.) these can be reset here
- WaveThern read: reading of the current temperature of a Wavetherm device
- Generic read RSSI: this field allows we to read the RSSI between the Wavenis communication concentrator (Titan router) and a remote device. If boosters are used, the RSSI should be indicated at the end. For example, if we wish to read a Wavenis device using boosters 3 and 5, by specifying the value ‘010203040506;3;5’, the RSSI between booster 5 and the MAC device 010203040506 will be given
- Generic read battery counter: this field allows we to obtain an estimation of the remaining battery life