Tunnel – Sending GPS positions, temperature and trailer opening detection for cold chain monitoring
¿Buscas alguna otra cosa?
Scenario details:
- We have a freezer truck transporting frozen goods. We need to install a GPS location device that also allows to monitor the temperature of the truck as well as to control its door
- For that, the GPS location device must check the GPS location each 60 seconds and send it to a central server via MQTT. In the sent data there must be a field with the temperature (the temperature sensor must have a temperature range from -50ºC to 80ºC). We also need to check the opening of the truck door. In case there is an opening, the system must gather the information about the opening time (date/time) and send the GPS position where the opening was made
- The truck will drive by places with no 2G/3G/4G coverage. So we don’t lose any location, temperature or door opening data, the device must store all data on its flash memory in order to send them when there is 2G/3G/4G connectivity
Solution: MTX-Tunnel firmware + MTX-Java-IoT/MTX-Java-T/MTX-Java-T2 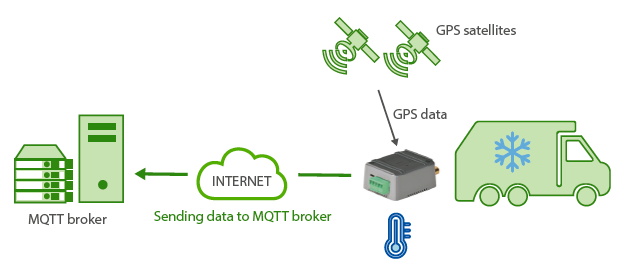 EXAMPLE of configuration (config.txt file) for the indicated scenario. Solution for quick communication via Socket TCP:
EXAMPLE of configuration (config.txt file) for the indicated scenario. Solution for quick communication via Socket TCP:
| Configuration | Observations |
| COMM_baudrate: 9600 COMM_bitsperchar: 8 COMM_autocts: off COMM_autorts: off COMM_stopbits: 1 COMM_parity: none COMM_power: on COMM2_baudrate: 9600 COMM2_bitsperchar: 8 COMM2_autocts: off COMM2_autorts: off COMM2_stopbits: 1 COMM2_parity: none GPRS_apn: movistar.es GPRS_login: MOVISTAR GPRS_password: MOVISTAR GPRS_timeout: 0 GPS_mode: logger GPS_period: 60 TEMPERATURE_enabled: on TEMPERATURE_period: 0 MTX_mode: none MTX_pin: 0000 MTX_model: MTX-4G-JAVA-IOT-STD-N-GPS MTX_atLimited: off MTX_numGSMErrors: 180 MTX_ping: 30 MTX_pingIP: 8.8.8.8 MTX_redLed: gps MTX_TPServer: es.pool.ntp.org MTX_TPServer2: 2.europe.pool.ntp.org MTX_TPProtocol: ntp SMS_allPhones: on SMS_sendIP: on SMS_ATEnabled: on SMS_ATResponse: on FIREWALL_enabled: off TELNET_enabled: on TELNET_login: user TELNET_password: 1234 TELNET_port: 20023 |
Serial port baud rate 8 bit data No flow control No flow control 1 stop bit No parity Activation of the port power lines Serial port baud rate 8 bit data No flow control No flow control 1 stop bit No parity APN GPRS provided by the GSM operator GPRS Login GPRS Password Permanent 3G session GPS working vía logger Attempt to send GPS location every 60 sconds Temperature sensor enabled Temperature will be read along with GPS We will not use TCP serial port gateways The SIM card PIN (if there is any) MTX modem model being used No limits for AT commands N. of GSM errors to reset Ping every 30 minutes without comms IP address to ping Red LED lights when there’s NO valid GPS location Time server 1 Time server 2 Time synch protocol Commands SMS sent from any mobile phone The modem will send IP to a missed call or SMS It is possible to send commands to MTX via SMS SMS replies to sent AT commands Any incoming connection form any IP is allowed Telnet is activated Telnet login Telnet password Port chosen for Telnet |
Details:
- Connections: the modem MTX-4G-Java-IoT-STD-N-GPS has a serial port in the DB9 connector. That’s where the temperature sensor MTX-TEMP-RS232 will be connected. Both devices are DCE (DB9 female) so you will need a converter Null-Modem DB9-DB9.
To detect if the door is open/closed we will use digital input GPIO2. According to the table in AnnexA, it corresponds with PIN 11 of MTX’s DB15. That is, if we connect the PIN 11 to PIN 14 of DB15 the modem will think that input has a “1” (for instance, open door) and if PIN 11 is not connected to anything the modem will think that input has a “0” (for instance, closed door) - With the previous configuration, 3 data frames will be sent. The first one is “TYPE”:”GPS” with the location data gathered every 60 seconds. This is an example:
{“IMEI”:354033090128458,”TYPE”:”GPS”,”P”:””,”DATE”:”2019/01/13”,”TIME”:“11:35:30”,”LAT”:”41.62964”,”NS”:”N”,”LON”:”2.361005”,”EW”:”E”,”ALT”:“187.9”,”SPE”:”0”,”COU”:”000.0”,”STA”:”3”,”HPO”:”1.2”,”VDO”:”1.9”,”SAT”:“08”,”TEMP”:”16.9”}
Where:
IMEI: the unique identification number of the modem
TYPE: JSON type (GPS in this case)
DATE: UTC date returned via GPS
TIME: UTC time returned via GPS
LAT: GPS Latitude
NS: N=North, S=South
LON: GPS Longitude
EW E=East , W=West
ALT: Altitude (meters)
SPE: Speed (km/h)
COU: Coure
STA: Status. 0=no Fix, 2=2D, 3=3D
HPO: Horizontal accuracy indication. The lower the better
VDO: Vertical accuracy indication. The lower the better
SAT: satellite
Nº TEMP: temperature read from the temperature sensor
The second data frame kind happens when there’s a change in the digital input 2 that controls if the door is open or closed. This data frame “TYPE”:”IOS” will send E/S data (digital I/Os, analog inputs) and the GPS location at those moments as well as the temperature. For example:
{“IMEI”:354033090128458,”TS”:”13/01/19 10:45:40”,”TYPE”:”IOS”,”P”:””,”IO1”:0,”IO2”:1, ”IO3”:0,”IO4”:0,”IO5”:0,”IO6”:0,“IO7”:0,”IO8”:0,”IO9”:0,”IO10”:0,”AD1”:1259, ”AD2”:1333,”CO1”:”1”,”CO2”:”3”,“CO3”:”3”,”GPSDATA”:{“DATE”:”2019/01/13”,”TIME”: ”10:45:41”,”LAT”:“41.62964”,”NS”:”N”,”LON”:”2.36099”,”EW”:”E”,”ALT”:”195.2”,”SPE”:”0”, “COU”:”000.0”,”STA”:”3”,”HPO”:”1.3”,”VDO”:”2.3”,”SAT”:”07”,”TEMP”:”16.4”}}
IMEI: the unique identification number of the modem
TYPE: JSON type (IOS in this case)
TS: TimeStamp (modem time when the event happened)
IOx: digital input x value
ADx: analog input x value
COx: pulse counter x value
GPSDATA.DATE: date given by GPS module
GPSDATA.TIME: time given by GPS module
GPSDATA.LAT: GPS latitude
GPSDATA.NS: N=North, S=South
GPSDATA.LON: GPS longitude
GPSDATA.EW: E=East, W=West
GPSDATA.ALT: altitude
GPSDATA.SPE: speed (km/h)
GPSDATA.COU: course
GPSDATA.STA: status, 0=no Fix, 2=2D, 3=3D
GPSDATA.HPO: horizontal precision, the lower the better
GPSDATA.VDO: vertical precision, the lower the better
GPSDATA.SAT: how many satellites are being used
GPSDATA.TEMP: temperature read from the temperature sensor
Note there are 2 hours back in the JSON. One in the TS field (modem time) and another one in the GPS data (GPS module time). There can be a difference in seconds due to the moment when the data is read.
The third kind of data frame that is produced are the DNS data frames. These data frames are configured (DNS_period) to be sent every 120 seconds. They show important information about the device time, its IP address, GSM coverage, technology used, digital and analog E/S status, GPS location, temperature, meter boxes and information regarding the GSM used.
This data frame is very interesting for several reasons. On one hand, the data frame shows data in real time. Sometimes, when the vehicle drives through areas with low GPS coverage (due to weather, geography), this DNS data frame is useful because supports information from the CID field, and that’s why it is possible to obtain the approximate location of the vehicle thanks to GSM location. It is also useful in areas of low 2G/3G/4G coverage. In case of long time periods, a lot of data is storaged until coverage is back. During those minutes we can still receive the GPS location information in real time thanks to the DNS data frame, without the need to wait to download the pending history.
Example of the DNS data frame:
{“IMEI”:354033090128458,”TYPE”:”DNS”,”TS”:”13/01/19 11:58:36”,”P”:””,”IP”:”95.12 4.172.178”,”CSQ”:14,”TECH”:”4g”,”VER”:”10.04”,”AUX”:””,”MOD”:”MTX-4G-JAVA-IOT-STDN-GPS”,”VCC”:12000,”IO1”:0,”IO2”:0,”IO3”:0,”IO4”:0,“IO5”:0,”IO6”:0,”IO7”:0,”IO8”:0,”IO9”:0,”IO10”:0, “AD1”:1284,”AD2”:1333,”GPSDATA”:{“DATE”:”2019/01/13”,”TIME”:”11:58:37”,“LAT”: ”41.62964”,”NS”:”N”,”LON”:”2.361005”,“EW”:”E”,”ALT”:”187.9”,”SPE”:”0”,”COU”:“000.0”, ”STA”:”3”,”HPO”:”1.3”,”VDO”:”1.8”,“SAT”:”07”,”TEMP”:”16.9”},”CO1”:”1”,”CO2”:“3”,”CO3”: ”3”,”CID”:”07;21E0;13B6D0A;87;--”}
IMEI: the unique identification number of the modem
TYPE: JSON type (IOS in this case)
TS: TimeStamp (modem time when the event happened)
IP: modem IP address
CSQ: modem coverage (0 … 31)
TECH: technology used in that moment (2G/3G/4G)
VER: MTX-Tunnel firmware version
MOD: MTX model (field MTX_model)
VCC: MTX supply voltage (in millivolts)
IOx: digital input x value
ADx: analog input x value
COx: pulse counter x value
CID: cell ID of the telephone station used
GPSDATA.DATE: date given by GPS module
GPSDATA.TIME: time given by GPS module
GPSDATA.LAT: GPS latitude
GPSDATA.NS: N=North, S=South
GPSDATA.LON: GPS longitude
GPSDATA.EW: E=East, W=West
GPSDATA.ALT: altitude
GPSDATA.SPE: speed (km/h)
GPSDATA.COU: course
GPSDATA.STA: status, 0=no Fix, 2=2D, 3=3D
GPSDATA.HPO: horizontal precision, the lower the better
GPSDATA.VDO: vertical precision, the lower the better
GPSDATA.SAT: how many satellites are being used
GPSDATA.TEMP: temperature read from the temperature sensor
